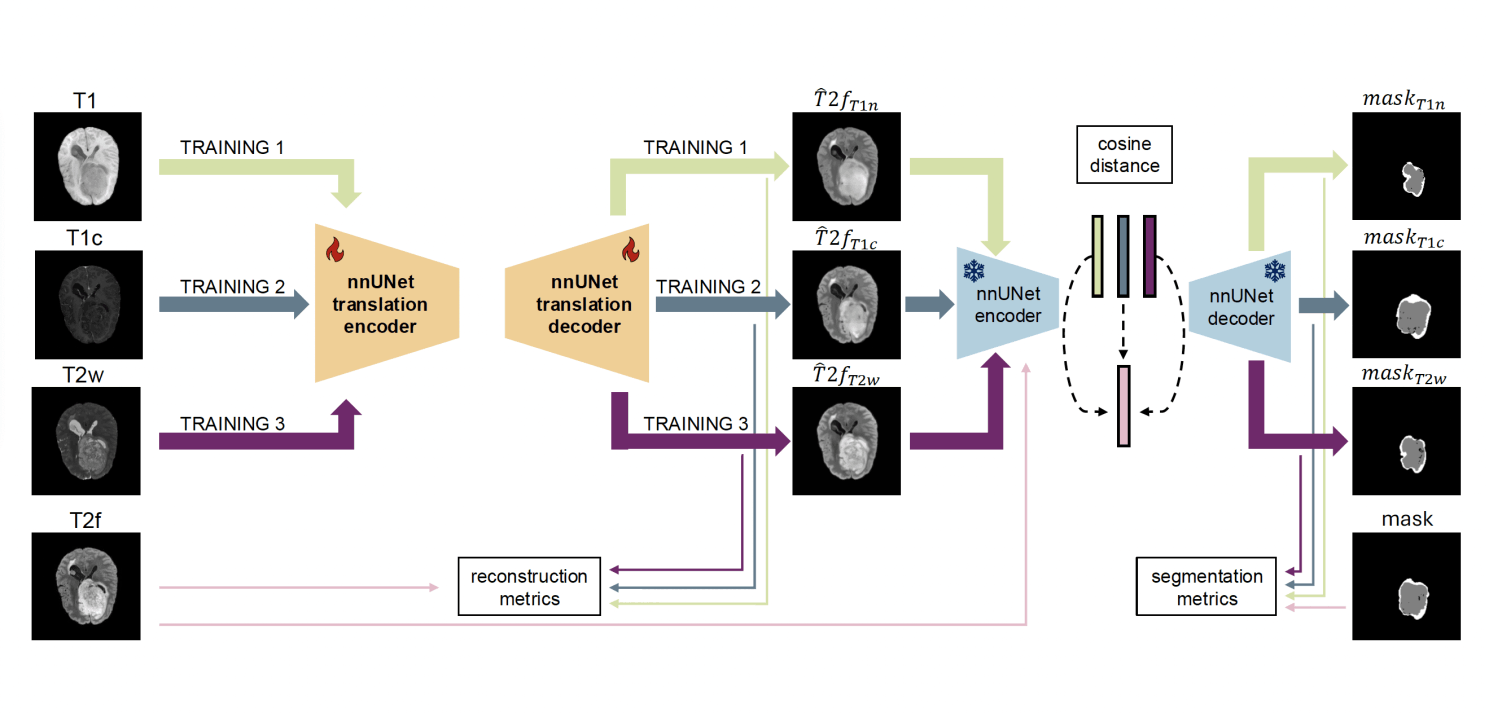
Missing modalities pose a persistent challenge in multi-modal brain MRI analysis, particularly for brain tumor segmentation. While recent methods address cross-modality synthesis, they often emphasize reconstruction fidelity over segmentation effectiveness.We propose a unified framework to assess the segmentation utility of synthetic modalities and their alignment with real counterparts in deep feature space. Using 3D nnU-Net based translation and segmentation networks, we perform exhaustive pairwise synthesis across four standard MRI sequences (T1n, T1c, T2w and T2f) on a dataset of 1251 glioma patients with full modality coverage and expert-labeled segmentation masks. Each synthetic modality is evaluated using reconstruction metrics (NMSE, SSIM and PSNR), segmentation performance (Dice and HD95), and feature space similarity (cosine distance, Fréchet distance and L2 norm). This design enables a holistic analysis of whether synthetic modalities retain task-relevant information and how closely they align with real-image embeddings. Our findings offer practical insights into MRI modality imputation, identifying which sequences are more suitable for synthesis and accurate segmentation.

Overview of our approach using T2f as target. Synthetic T2f images are generated from T1n, T1c, and T2w using a nnU-Net based translation model, and are then evaluated via segmentation performance and feature-space similarity using encoder embeddings. The process is repeated using each modality as target, resulting in 12 models in total. Subscripts in the format target_source (e.g., T2f_T1n) denote the synthetic image of the target modality generated from the source modality.
Comprehensive cross-modality synthesis. Built 3D nnU-Net models to perform all pairwise translations among four standard brain MRI modalities (T1n, T1c, T2w, T2f).
Segmentation impact evaluation. Assessed how using synthesized modalities instead of real ones affects brain tumor segmentation performance.
Feature-space similarity analysis. Compared deep feature embeddings of real vs. synthetic modalities to study representational alignment and modality transferability.
Link to the publication: - on press -
Reference:
@inproceedings{diana-albelda25,
title={Multi-modal Brain MRI Synthesis with nnU-Net: Exploring Segmentation Performance and Cross-Modality Relationships},
author={Diana-Albelda, Cecilia and Longuefosse, Arthur and García-Martín, Álvaro and Bescos, Jesus},
booktitle={International Workshop on Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging},
pages={},
year={2025},
organization={Springer}
}
Offline Website Builder